Mengenal Penyakit Hipertensi Pulmonal Fokus pada Terapi Oksigen (bag.I)
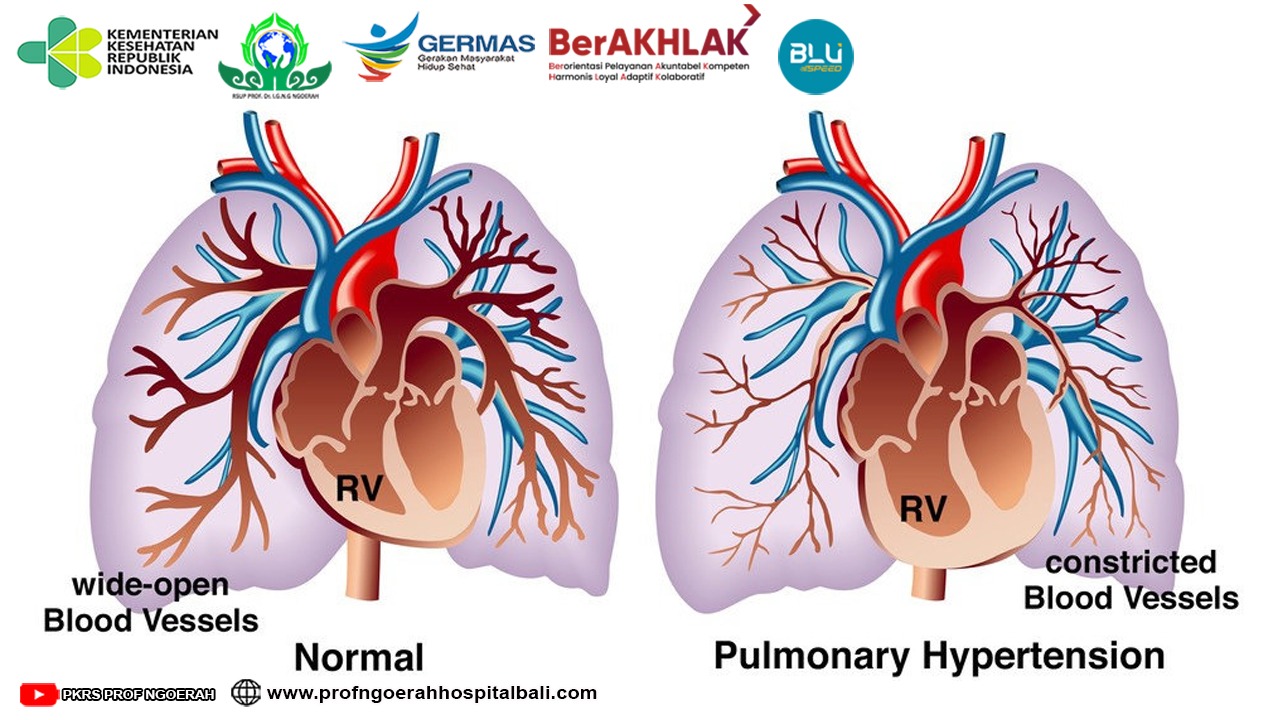
Pasien-pasien dengan hipertensi khususnya Hipertensi Pulmonal (HP) serta dengan manifestasi penyakit paru obstruktif kronik (PPOK) harus mendapatkan tatalaksana PPOK secara optimal sesuai dengan guideline GOLD <!--[if supportFields]>ADDIN CSL_CITATION { "citationItems" : [ { "id" : "ITEM-1", "itemData" : { "author" : [ { "dropping-particle" : "", "family" : "Diagnosis", "given" : "Copd", "non-dropping-particle" : "", "parse-names" : false, "suffix" : "" }, { "dropping-particle" : "", "family" : "To", "given" : "Pocket Guide", "non-dropping-particle" : "", "parse-names" : false, "suffix" : "" } ], "id" : "ITEM-1", "issued" : { "date-parts" : [ [ "2013" ] ] }, "title" : "Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung", "type" : "article-journal" }, "uris" : [ "http://www.mendeley.com/documents/?uuid=34b4ad7d-357b-4d67-8494-64fe2b4e16bc" ] } ], "mendeley" : { "previouslyFormattedCitation" : "(9)" }, "properties" : { "noteIndex" : 0 }, "schema" : "https://github.com/citation-style-language/schema/raw/master/csl-citation.json" }<![endif]-->(1)<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]-->. Tujuan terapi adalah perbaikan dari gejala klinis, status hemodinamik, fungsi ventrikel kanan dan akhirnya peningkatan kualitas hidup dan angka harapan hidup. Terapi oksigen adalah terapi utama pada HP dan PPOK. Karena HP pada PPOK biasanya ringan dan sedang, terapi medikamentosa yang lain menjadi kontroversial. Pada sisi yang lain pemberian terapi medikamentosa dapat dipertanggung jawabkan karena bahkan pada HP yang ringan dapat menjadi berat saat terjadi eksaserbasi PPOK, yang dapat meningkatkan mPAP serta memberikan kontribusi terjadinya gagal jantung kanan <!--[if supportFields]>ADDIN CSL_CITATION { "citationItems" : [ { "id" : "ITEM-1", "itemData" : { "ISSN" : "1178-2005", "PMID" : "19802350", "abstract" : "Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is the hemodynamic manifestation of various pathological processes that result in elevated pulmonary artery pressures (PAP). The National Institutes of Health Registry defined pulmonary arterial hypertension as the mean PAP of more than 25 mm Hg with a pulmonary capillary wedge pressure or left atrial pressure equal to or less than 15 mm Hg. This definition remains the currently accepted definition of PH that is used to define PH related to multiple clinical conditions including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The estimated US prevalence of COPD by the National Health Survey in 2002 in people aged >25 was 12.1 million. There is a lack of large population-based studies in COPD to document the correct prevalence of PH and outcome. The major cause of PH in COPD is hypoxemia leading to vascular remodeling. Echocardiogram is the initial screening tool of choice for PH. This simple noninvasive test can provide an estimate of right ventricular systolic and right atrial pressures. Right heart catheterization remains the gold standard to diagnose PH. It provides accurate measurement of mean PAP and pulmonary capillary wedge pressure. Oxygen therapy remains the cornerstone therapeutic for hypoxemia in COPD patients. Anecdotal reports suggest utility of PDE5-inhibitors and prostacyclin to treat COPD-related PH. Large randomized clinical trials are needed before the use of these drugs can be recommended.", "author" : [ { "dropping-particle" : "", "family" : "Jyothula", "given" : "Soma", "non-dropping-particle" : "", "parse-names" : false, "suffix" : "" }, { "dropping-particle" : "", "family" : "Safdar", "given" : "Zeenat", "non-dropping-particle" : "", "parse-names" : false, "suffix" : "" } ], "container-title" : "International journal of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease", "id" : "ITEM-1", "issued" : { "date-parts" : [ [ "2009", "1" ] ] }, "page" : "351-63", "title" : "Update on pulmonary hypertension complicating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.", "type" : "article-journal", "volume" : "4" }, "uris" : [ "http://www.mendeley.com/documents/?uuid=235c9742-9c2a-4525-9513-679b801ca99b" ] }, { "id" : "ITEM-2", "itemData" : { "DOI" : "10.4103/2045-8932.83444", "ISSN" : "2045-8940", "PMID" : "22034603", "abstract" : "There have been tremendous strides in the management of pulmonary hypertension over the past 20 years with the introduction of targeted medical therapies and overall improvements in surgical treatment options and general supportive care. Furthermore, recent data shows that the survival of those with pulmonary arterial hypertension is improving. While there has been tremendous progress, much work remains to be done in improving the care of those with secondary forms of pulmonary hypertension, who constitute the majority of patients with this disorder, and in the optimal treatment approach in those with pulmonary arterial hypertension. This article will review general and targeted medical treatment, along with surgical interventions, of those with pulmonary hypertension.", "author" : [ { "dropping-particle" : "", "family" : "Stamm", "given" : "Jason a", "non-dropping-particle" : "", "parse-names" : false, "suffix" : "" }, { "dropping-particle" : "", "family" : "Risbano", "given" : "Michael G", "non-dropping-particle" : "", "parse-names" : false, "suffix" : "" }, { "dropping-particle" : "", "family" : "Mathier", "given" : "Michael a", "non-dropping-particle" : "", "parse-names" : false, "suffix" : "" } ], "container-title" : "Pulmonary circulation", "id" : "ITEM-2", "issue" : "2", "issued" : { "date-parts" : [ [ "0" ] ] }, "page" : "138-59", "title" : "Overview of current therapeutic approaches for pulmonary hypertension.", "type" : "article", "volume" : "1" }, "uris" : [ "http://www.mendeley.com/documents/?uuid=68e472f4-30b7-495d-9b51-a87a37011dd4" ] } ], "mendeley" : { "previouslyFormattedCitation" : "(2,10)" }, "properties" : { "noteIndex" : 0 }, "schema" : "https://github.com/citation-style-language/schema/raw/master/csl-citation.json" }<![endif]-->(2)<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]-->. Terapi medikamentosa dibagi menjadi vasodilator spesifik dan nonspesifik. Jika didapatkan kegagalan pada terapi medikamentosa makan terapi invasif dan modalitas terapi baru menjadi pilihan terapi berikutnya.
Optimalisasi penganganan PPOK sesuai guideline GOLD adalah kunci utama daripada penatalaksanaan umum. Asap rokok adalah penyebab paling sering terjadinya PPOK. Banyak penelitian melaporkan perbaikan gejala, fungsi paru, morbiditas dan mortalitas pasien PPOK setelah berhenti merokok <!--[if supportFields]>ADDIN CSL_CITATION { "citationItems" : [ { "id" : "ITEM-1", "itemData" : { "id" : "ITEM-1", "issued" : { "date-parts" : [ [ "0" ] ] }, "title" : "pathophysiology and clinical implication.pdf", "type" : "article" }, "uris" : [ "http://www.mendeley.com/documents/?uuid=99880bf6-a104-49a5-ba6e-83a6b929d156" ] } ], "mendeley" : { "previouslyFormattedCitation" : "(11)" }, "properties" : { "noteIndex" : 0 }, "schema" : "https://github.com/citation-style-language/schema/raw/master/csl-citation.json" }<![endif]-->(3,4)<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]-->. Program rehabilitasi ikut menjadi bagian dari penatalaksanaan umum, karena dapat meningkatkan kapasitas fungsional pasien. Program ini sebaiknya segera dimulai setelah PPOK terkontrol.
Panduan penatalaksanaan PPOK merekomendasikan pemberian terapi oksigen jika PaO2 <55>Long Term Oxygen Therapy (LTOT) meningkatkan angka harapan hidup pasien. Pemberian oksigen hanya pada saat aktivitas atau eksaserbasi memberikan efek yang minimal dalam memperbaiki kualitas hidup. Reversibilitas HP setelah pemberian oksigen saat serangan eksaserbasi PPOK menunjukkan perbaikan keluaran jangka panjang, meningkatkan kemampuan aktivitas, menurunkan mPAP serta PVR dan dapat meningkatkan fungsi ventrikel kanan (5,6,<!--[if supportFields]>ADDIN CSL_CITATION { "citationItems" : [ { "id" : "ITEM-1", "itemData" : { "DOI" : "10.1513/pats.200407-037MS", "ISSN" : "1546-3222", "PMID" : "16113464", "abstract" : "Pulmonary hypertension is a common complication of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The increase in pulmonary artery pressures is often mild to moderate. However, 5-10% of patients with advanced COPD may suffer from severe pulmonary hypertension and present with a progressively downhill clinical course because of right heart failure added to ventilatory handicap. The prevalence of clinically significant severe pulmonary hypertension in COPD is roughly estimated to be of 1-2/1,000. The cause of pulmonary hypertension in COPD is generally assumed to be hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction leading to permanent medial hypertrophy. However, recent pathologic studies point rather at extensive remodeling of all layers of the pulmonary arterial walls. These aspects account for minimal reversibility with supplemental oxygen. There may be a case for pharmacologic treatment of pulmonary hypertension in selected patients with advanced COPD and right heart failure. However, it will be a challenge for randomized controlled trials to overcome the difficulties of the diagnosis of right ventricular failure and the definition of a relevant primary endpoint in pulmonary hypertensive patients with COPD.", "author" : [ { "dropping-particle" : "", "family" : "Naeije", "given" : "Robert", "non-dropping-particle" : "", "parse-names" : false, "suffix" : "" } ], "container-title" : "Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society", "id" : "ITEM-1", "issue" : "1", "issued" : { "date-parts" : [ [ "2005", "1" ] ] }, "page" : "20-2", "title" : "Pulmonary hypertension and right heart failure in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.", "type" : "article-journal", "volume" : "2" }, "uris" : [ "http://www.mendeley.com/documents/?uuid=5c451c99-9fe6-4154-b35a-6cddf52dd61f" ] } ], "mendeley" : { "manualFormatting" : "7)", "previouslyFormattedCitation" : "(12)" }, "properties" : { "noteIndex" : 0 }, "schema" : "https://github.com/citation-style-language/schema/raw/master/csl-citation.json" }<![endif]-->7)<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]-->.
Pada Medical Research Council Trial didapatkan bahwa angka mortalitas dalam 5 tahun sebesar 67% pada pasien tanpa terapi oksigen dan 47% pada pasien dengan terapi oksigen 15jam/hari. Pemeriksaan kateterisasi jantung kanan ulangan setelah 500 hari menunjukkan rerata kenaikan mPAP 2,7 mmHg/tahun pada kelompok pasien tanpa terapi oksigen. Pada kelompok pasien dengan LTOT didapatkan nilai mPAP yang tetap stabil, hal ini dapat dijelaskan bahwa LTOT mengurangi vasokonstriksi pembuluh darah paru sehingga mencegah terjadinya vessel remodeling, reduksi PVR dan mPAP sehingga mengurangi beban ventrikel kanan dan akhirnya memperbaiki vitalitas <!--[if supportFields]>ADDIN CSL_CITATION { "citationItems" : [ { "id" : "ITEM-1", "itemData" : { "DOI" : "10.1016/j.ccl.2012.03.005.Right", "author" : [ { "dropping-particle" : "", "family" : "Manuscript", "given" : "Author", "non-dropping-particle" : "", "parse-names" : false, "suffix" : "" } ], "id" : "ITEM-1", "issue" : "2", "issued" : { "date-parts" : [ [ "2013" ] ] }, "page" : "243-256", "title" : "NIH Public Access", "type" : "article-journal", "volume" : "30" }, "uris" : [ "http://www.mendeley.com/documents/?uuid=ba2be94e-ef01-4bd2-906b-bbba3bfa8ec3" ] } ], "mendeley" : { "manualFormatting" : "(5,6,7)", "previouslyFormattedCitation" : "(6)" }, "properties" : { "noteIndex" : 0 }, "schema" : "https://github.com/citation-style-language/schema/raw/master/csl-citation.json" }<![endif]-->(5,6,7)<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]-->.
Rendahnya kadar oksigen dalam darah, obstruksi saluran napas ditambah berkurangnya kekuatan otot pernapasan yang terjadi saat tidur menyebabkan desaturasi kadar oksigen pada malam hari. Episode ini terjadi pada fase non rapid eye movement dan lebih nyata pada fase rapid eye movement. Hipotesis mengatakan bahwa desaturasi oksigen pada malam hari dapat menyebabkan atau memperberat HP. Hipotesa ini belum terbukti sehingga keuntungan pemberian Nocturnal Oxygen Therapy (NOT) belum tertera dalam guideline. Fletcher et al. dan Chaouat et al.1992 melaporkan bahwa tidak terdapat perbedaan angka harapan hidup pasien PPOK yang mendapat oksigen 3liter/jam selama tidur dengan kelompok control. Tetapi dilaporkan perbaikan hemodinamik dengan penurunan rerata mPAP sebesar 3,7 mmHg pada kelompok NOT. Pasien COPD dengan desaturasi oksigen saat tidur, tetapi memiliki oksigenisasi yang adekuat saat siang hari atau aktivitas disarankan untuk dievaluasi kemungkinan adanya obstructive sleep apnea (4,6-8).
Para sobat sehat kami mengharapkan dapat berkonsultasi kembali dengan para pakar atau ahli di bidangnya misal dalam bidang penyakit dalam, sehingga pasien pasien dengan HP memperoleh segala manfaat dari yang kita berikan terutama dengan terapi oksigen ini.
Daftar Pustaka:
Elwing J, Panos RJ. Pulmonary hypertension associated with COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis.2008;3(1):55–70.
Jyothula S, Safdar Z. Update on pulmonary hypertension complicating chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2009;4:351–63.
McLaughlin V V, Archer SL, Badesch DB, Barst RJ, Farber HW, Lindner JR, et al. ACCF/AHA 2009 expert consensus document on pulmonary hypertension: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Expert Consensus Documents and the American Heart Association: developed in collaboration with the American College . Circulation. 2019;119:2250–94.
Chaouat a, Naeije R, Weitzenblum E. Pulmonary hypertension in COPD. Eur Respir J. 2008;32:1371–85.
Shujaat A, Bajwa A a, Cury JD. Pulmonary hypertension secondary to COPD. Pulm Med. 2012;2012:203952.
Todd M,Kolb, Hassoun P. Right ventricular dysfunction in Chronic Lung Disease.Cardiol Clin.2013;30:243–56.
Minai O a, Chaouat A, Adnot S. Pulmonary hypertension in COPD: epidemiology, significance, and management: pulmonary vascular disease: the global perspective. Chest. 2010;137:39S–51S.
<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]-->







